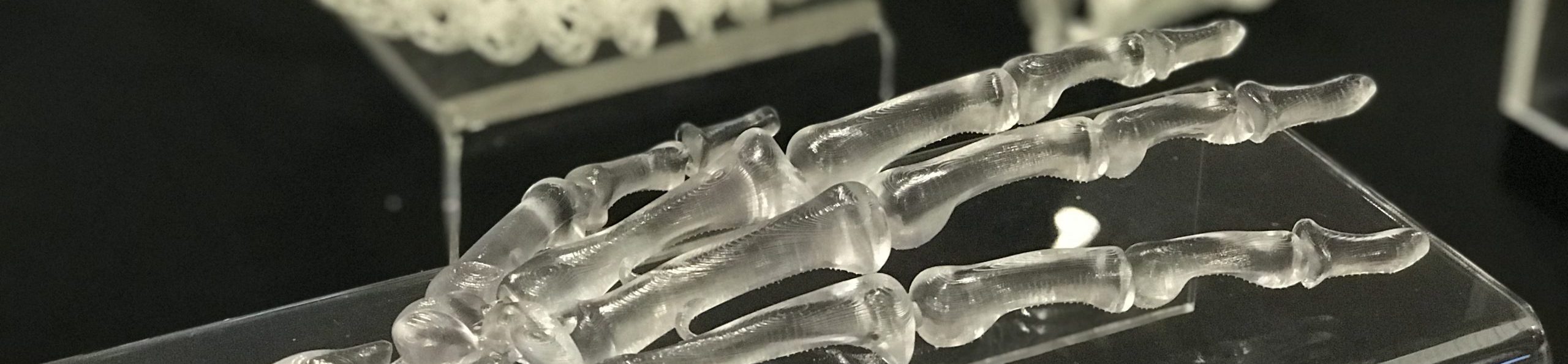
3D Printing of Titanium Implant with Interconnected Pore Structures
________________________________________
Problem Statement
Presently, stainless steel and titanium alloys are the most commonly used implant materials for orthopaedic applications. Stainless steel has a risk of nickel toxicity leading to allergic reactions within the human body. Both non-biodegradable titanium and stainless-steel implants may require revision surgery to remove the implants after the wound healing process. Stress shielding effects arising due to the mismatch in the Young’s modulus values between the bone and the implant poses a major threat contributing to revision surgery. Therefore, it is of primary importance to adjust the Young’s modulus of implants by careful selection of biomaterials.
Objective
This project aims to design, develop, and manufacture new semi-degradable titanium-magnesium (Ti-Mg) composites utilising inkjet 3D printing of porous Ti parts followed by pressureless infiltration of Mg into Ti parts. The new porous implant design mimics natural bone structure to bring closer the Young’s modulus of implant vs bone. Using this newly proposed approach, the 3D printed porous Ti-Mg implant could aid in faster healing and leave with the remaining metal structure within the body.
Key Benefits/ Outcomes
- NUS designed and printed three implant structures (cubic, octet, TPMS) with varying porosity (40-60%, pore by design) for bone implant applications and established the correlation of porosity vs. Young’s Modulus. This will be filed as an Invention Disclosure by the research team.
- SIMTech successfully developed the Mg infiltration process of Mg into the 3D printed Ti implants. Based on SEM & EDX, Mg is well distributed in the pores of the Ti implant.
- With superior mechanical properties, low Young’s modulus (5.2GPa) and average pore size closer to 100μm (pore by process), the 3D printed Ti+Mg composite demonstrates a promising prospect in the load-bearing biomedical applications.
- Based on all in-vitro cell toxicity tests comparing Ti vs. Ti-Mg samples, it is proven that Mg is effective in reducing stress in cells and reducing cell death. The release of Mg2+ ions from the Ti-Mg composite is beneficial to bone formation and the healing process.